近日,植物学顶尖杂志Molecular Plant在线发表浙江大学农学院樊龙江教授团队题为“PlantcircBase: a database forplant circular RNAs”研究文章,建立了国际上首个植物circRNA数据库。该数据库提供了最为完整的植物circRNA基因集和circRNA-miRNA-mRNA互作信息、circRNA可视化、circRNA预测等工具。
circRNA是一类呈封闭环状结构的、不易被RNA外切酶降解的非编码RNA分子,是近年来RNA研究领域的一个热点。其实早在30多年前circRNA已被发现,但是由于实验条件与技术的限制,最初的circRNA被认为是转录的“垃圾”和“噪音”。直到近5年,circRNA的合成机制和功能才慢慢被揭示。研究发现circRNA的其中一个重要功能是作为miRNA海绵(miRNA sponge):由于circRNA序列上富含miRNA结合位点,可以在细胞中结合相应的miRNA,从而影响miRNA靶基因的表达水平。然而,目前大部分关于circRNA的研究集中在人类和动物上,对于植物circRNA研究非常少。
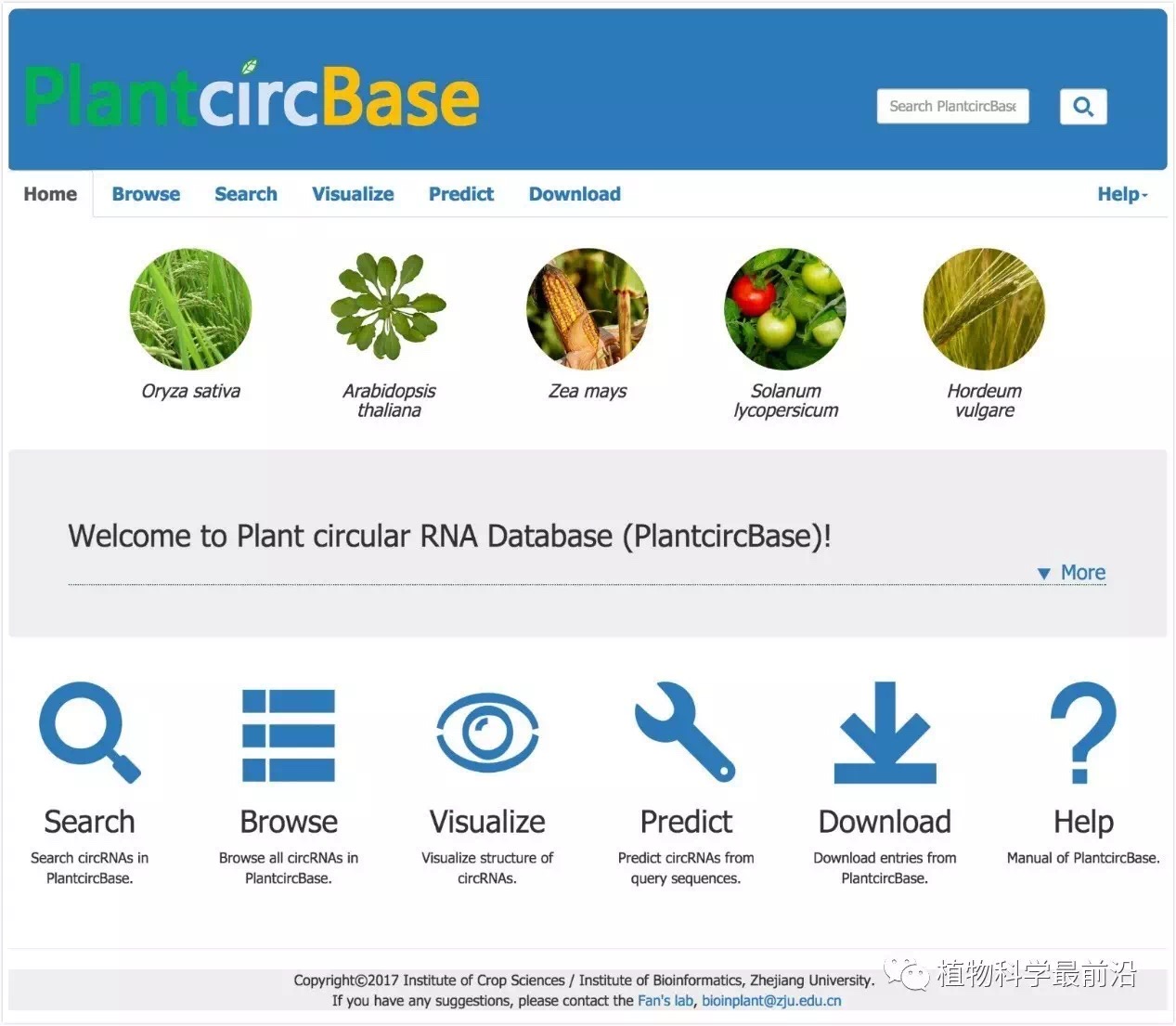
图1 PlantcircBase主页(http://ibi.zju.edu.cn/plantcircbase/)
樊龙江教授团队结合生物信息学与作物学专业优势,紧跟研究前沿,近年来在植物circRNA领域取得一系列成果:
(1)由于目前主要circRNA鉴定方法都是根据人类和动物基因组设计,不同方法之间在植物上预测的重复性很差,因此考虑到植物与动物基因组和基因结构之间的特征差异,建立一个专门针对植物的circRNA鉴定方法和软件变得非常迫切,对植物后续的circRNA特征及功能研究非常重要。樊龙江教授团队为此开发了一个针对植物circRNA大规模鉴定的方法及其软件“PcircRNA_finder”,它可在植物中鉴定出高可信度的circRNA。这是第一个专门为植物设计的circRNA鉴定软件(Chen et al., 2016, Bioinformatics);
(2)目前所有的circRNA预测软件都只给出该circRNA的起始和终止位置,而circRNA内部的序列却无法确定(可能存在剪切、可变剪切等)。为此,该团队提出了一个拼接circRNA序列全长的方法及其软件“circseq-cup”。利用该方法对水稻circRNA全长序列的拼接和分析发现,水稻circRNA普遍存在可变剪切,并且剪切的位置大多在非GT/AG信号位点(非经典剪切位点),这与动物中circRNA的剪切位点大多在经典剪切位点(GT/AG)不同(Ye et al., 2016, RNA Biology);
(3)该团队在水稻和拟南芥基因组上大规模鉴定circRNA,首次阐述了circRNA在植物基因组中普遍存在,circRNA的表达与其母基因表达存在关联,并且circRNA在植物中的形成机制与动物和人类中有些不同(Ye et al., 2015, NewPhytologist)。
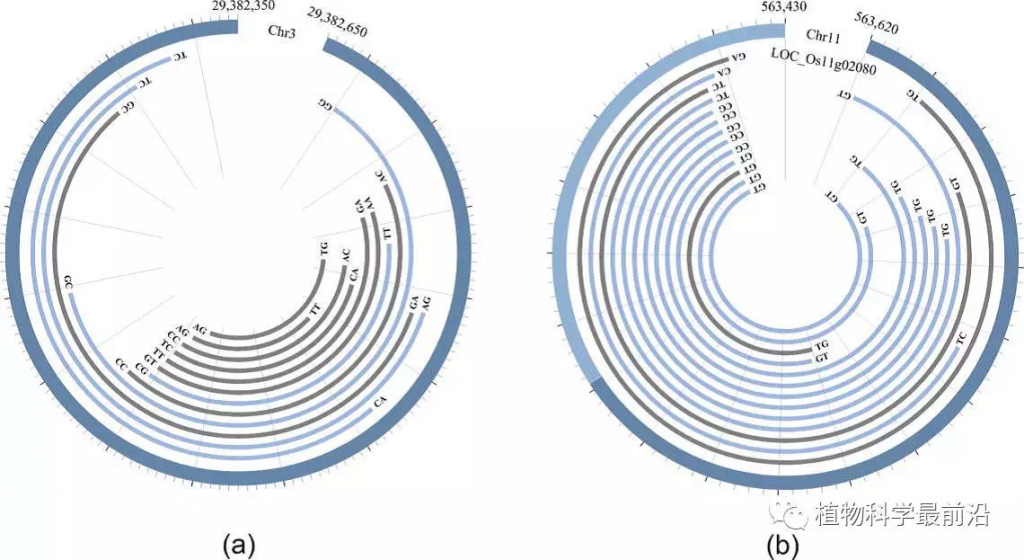
同时,针对水稻,该团队在其发育和产量形成的关键时期,大规模测定并鉴定circRNA,累计获得了4万多个水稻circRNA基因,这是目前最为完整的水稻circRNA基因集。为此,樊龙江教授团队结合自身团队鉴定的水稻和拟南芥circRNA和其他研究团队发表的植物circRNA数据,建立了植物上首个circRNA数据库“PlantcircBase”(http://ibi.zju.edu.cn/plantcircbase/)(Chu et al., 2017, Molecular Plant)。该数据库收集了已发表的水稻、拟南芥、玉米、番茄和大麦5个物种的circRNA数据,包括已经被实验验证的circRNA及其相应引物、circRNA-miRNA-mRNA互作信息等。除此之外,该数据库还提供circRNA可视化、circRNA预测等工具,为植物circRNA的后续研究提供了便捷和重要基础。
PlantcircBase: a database for plant circular RNAs
Qinjie Chu, Xingchen Zhang, Xintian Zhu, Chen Liu, Lingfeng Mao, Chuyu Ye, Qian-Hao Zhu, Longjiang Fan
Here, we created a database of plant circRNAs (termed as PlantcircBase; http://ibi.zju.edu.cn/plantcircbase/) for plant researchers. We have collected publicly available circRNAs identified in recent years by bioinformatics prediction and/or experimental validation from O. sativa, A. thaliana, Zea mays, Solanum lycopersicum and Hordeum vulgare (Wang et al, 2014; Ye et al., 2015; Lu et al., 2015; Ye et al., 2016; Supplemental Table 1), as well as unpublished circRNAs newly identified by this study. Based on the collected circRNAs, we further predicted those putatively acting as miRNA sponges and their potential networks involving circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in the corresponding organisms. Our database also provides other functions such as visualization of circRNA structures based on their genomic position and prediction of circRNAs from query sequences generated by Sanger sequencing or high-throughput sequencing. In order to provide the latest developments of circRNAs in plants, we will update PlantcircBase when newly identified plant circRNAs are available, and also plan to add new functionalities in the database in future, such as functions and biogenesis mechanisms of circRNAs.
上述成果发表的文章清单:
(1) Ye Chuyu, Chen Li, Liu Chen, Zhu Qian-Hao, Fan Longjiang. Widespread non-codingcircular RNAs in plants. New Phytologist, 2015 (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nph.13585/abstract)
(2) Chen Li, Yu Yongyi, Zhang Xingchen, Liu Chen, Ye Chuyu, Fan Longjiang.PcircRNA_finder: a software for circRNA prediction in plants. Bioinformatics,2016.(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=27493192)
(3) Ye Chuyu, Zhang Xingchen, Chu Qinjie, Liu Chen, Yu Yongyi, Jiang Weiqin, ZhuQian-Hao, Fan Longjiang, GuoLongbiao. Full length sequence assembly revealscircular RNAs with diverse non GT/AG splicing signals in rice. RNA Biology,2016.(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=27739910)
(4) Chu Qinjie, ZhangXingchen, Zhu Xintian, Liu Chen, Mao Lingfeng, Ye Chuyu, Zhu Qian-Hao, FanLongjiang. PlantcircBase: a database for plant circular RNAs. Molecular Plant,2017.(http://www.cell.com/molecular-plant/fulltext/S1674-2052(17)30074-6)
来源:植物科学最前沿



来第一个抢占沙发评论吧!